From years of teaching in rural, low-income areas in Central Illinois, and after being a product of one myself, I have seen and experienced the impact that deprivation can have on a child’s ability to learn. The biggest impact is on their motivation, their curiosity, and their perseverance through frustration. A kid who has been deprived of one or more needs struggles to see the point of school. But, even a kid who is fed, clothed, and has a place to sleep can still be majorly deprived of the needs a human being must have met to be successful. According to Dr. Abraham Maslow, a human being has needs that go just beyond the physical.
Credit : Simply Psychology
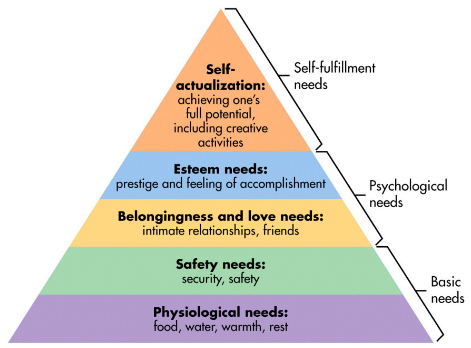
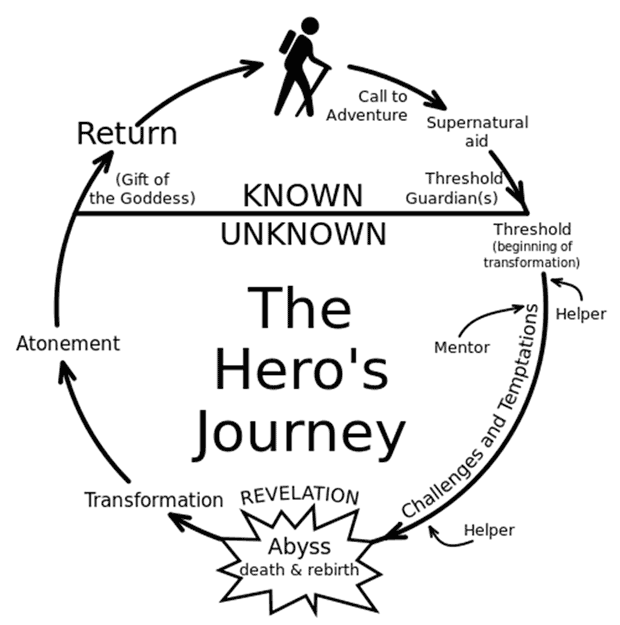
In fact, he formulated that there was a pyramid of needs, five tiers high, that built upon themselves to create total fulfillment. In the top tier, a person is capable of reaching the full potential of human beings, which Maslow called “Self-Actualization.” In order to produce, create, and find the drive to do so, a person must reach the fifth tier at the top of the needs pyramid, but Maslow stated that this could not happen until the bottom four tiers were met, each building on the foundation of the one below. In other words, until your most basic needs are met, it’s impossible to move to the next tier, and impossible to create.
Credit: WikiCommons
Hierarchy of Needs
BASIC NEEDS
- Physiological Needs- water, food, shelter, warmth
If we are expending all our energy on trying just to survive, we cannot expend energy on creative productivity.
It’s obvious that humans have physical needs (yes, including those physical needs… ya perv…) that are required just for survival. Humans need water, food, clothing, and shelter to survive, which is why makes up the first tier, the foundation of the pyramid of needs. Unfortunately, we live in a world, even in countries considered first world, that fail to provide these basic human rights to everyone. No progress can be made unless these basest of needs are being net, and met regularly, which is why the second tier is just as important as the first.
2. Security Needs- stability, consistency, healthcare, resources, employment
If we are expending all our energy trying to secure our resources, we cannot expend energy on creative productivity.
Human beings must have their basic needs met, and be comfortable that they will continue to be met. Living in constant fear of being hungry, cold, vulnerable, broke, creates toxic amounts of stress on the human body. This is why poverty is the root cause of so many health issues- the constant threat of losing everything in the blink of an eye. Many families in my school district are just skirting disaster, one unforeseen event, bill, accident away from collapse.
When living in this constant anxious state, toxic stress becomes a major obstacle. When unable to get out from under the stress, it leads to health issues from an impaired immune system, mental health issues such as depression and anxiety, and strain on relationships, personal and professional.
So, perhaps, your basic needs are being met, but just not consistently. Are you worried about your job security or struggling with unemployment? Is your health a constant battle for you, mental or physical? Are you worried about access the health care?
“Living in constant fear of being hungry, cold, vulnerable, broke, creates toxic amounts of stress on the human body.”
PSYCHOLOGICAL NEEDS
3. Socio-Emotional Needs- belonging, intimate relationships, affection, touch, family connections
If we are expending all our energy trying find a sense of belonging and identity, we cannot expend energy on creative productivity.
The biggest revelation I have had in my study of teaching children with trauma has been the impact of relationships on a child’s ability to learn and function socially. From the very first connection a baby makes with their caregivers, the roots of social, emotional, and physical needs are established. If these tiny humans establish healthy, trustworthy relationships with their caregivers, research shows that over the course of their life they will be better students, better regulators of stress and emotions, and better able to develop healthy relationships with others. Evidence has even shown that “problem” students can be helped, not with strict punishments and zero-tolerance policies, but simply by forming a trusting bond with an adult. This is especially true for children who have been deprived fulfilling relationships with their caregivers.
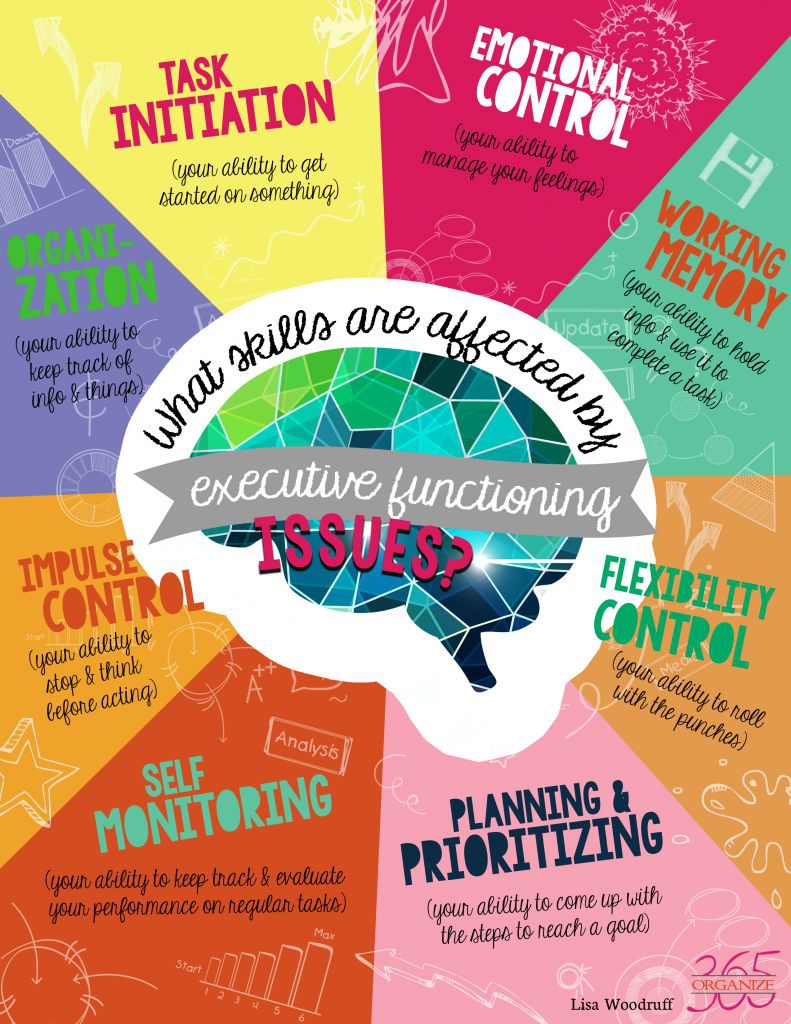
They also build the foundations of strong Executive Functions, or in other words, all those other things our brain does beyond problem solving and bodily functions. Executive functions include memory, organization, prioritizing and planning, task initiation, impulse control, flexibility, emotional control, and self monitoring. These are the areas of the brain that are critical for success in school. And, they’re the same skills needed to formulate a new idea, the creativity to develop it, and the motivation and inspiration to carry it through to the end. In essence, anyone who has experienced trauma has a higher chance of deficits in their executive functioning.
Credit: Lisa Woodruff
These executive functions are the same parts of the brain heavily impacted by Autism and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, meaning that exposure to trauma can have the same impact on learning and create the same deficits as ADHD and Autism.
It may seem like a far leap to say that your relationships directly impact your abilities to think and learn. After all, relationships are social and learning is cognitive. But, human beings are social animals. Our evolution has been heavily dependent upon our ability to build communities; they create security and safety in ancient and our modern times. We crave interaction and affection, and that in itself creates its own sense of security. Belonging is crucial. And, as discussed in the second tier of the hierarchy, security is important on the path to self-actualization.
This may be the area in your life that may have the least structural foundation, and may be the cause of your writing issues. Writers are a lonely lot. We are esoteric, eccentric, and many enjoy being alone, preferring to watch from the sidelines rather than participate in society. This can lead to feelings of isolation. If you’re struggling with rejection, identity, or building healthy relationships, that fear of loneliness may be impacting the creative processes. Rejection in your personal life can easily translate over into the fear that your creations (the purest expression of you) will be rejected too.
“Evidence has even shown that “problem” students can be helped, not with strict punishments and zero-tolerance policies, but simply by forming a trusting bond with an adult.”
4. Esteem Needs- Self image, confidence, mental health
If we are expending all our energy trying find a sense of belonging and identity, we cannot expend energy on creative productivity.
When the word self-esteem enters a conversation, even I will admit, I find it hard not to roll my eyes and sigh. It’s hard not to immediately conjure images of participation trophies and posters of kittens on “hanging in there” on ropes. But, while self-esteem has become a millennial buzzword in the extreme, it remains an important part of our mental health despite the obnoxious reputation the word has garnered. In this particular case, self-esteem refers to the image we have of ourselves in our own heads and how that impacts how we interact with other people and engage in activities because of it.
A person with healthy confidence will feel comfortable around others and when alone, knowing that a healthy balance can be found in in both. They will also have a healthy respect for themselves, be able to take constructive criticism, and be able to make positive choices for their life. They will know that they have self-worth simply because they are a human being and they deserve to have their needs met.
A person who is struggling with self-esteem, especially conditions resulting from abuse and neglect, will be in constant need to validate their self-worth. This validation can come in the form of many ways- praise, physical contact, attention, and other positive forms of interaction with people. In some cases, when the need for this validation is high but does not occur, the result can be mental disorders such as anxiety, depression, eating disorders, self harm, and/or drug addictions that develop out of a need to numb the pain of worthlessness.
The biggest issue that can be a result from lack of having self-esteem needs met, especially when pursuing creative projects, is imposter syndrome. This is the deep seated feeling that you are a talent-less fraud and a paranoia that you are about to be “outed” as a fraud the minute someone sees your work. This alone is the reason some people never share their artwork, their writing, or their creations with other people, even close family and friends. Ironically, the validation for that work is what they crave most, and would actually help.
Since this need is the most cerebral of the human needs, it tends to be the most overlooked area. You can see a person physically starving, but you can’t always see self-esteem issues until they manifest physically, such as the weight loss of an eating disorder. Another sad aspect of this issue is that because they suffer from worth issues, those suffering from low self-esteem are trapped in a vicious cycle of believing that it is okay for them to feel worthless, because in their skewed belief system, they are in fact worthless.
Does this sound like you? Are you terrified to let others see your creative work for fear of rejection or ridicule? Are you fighting a battle with depression, anxiety, eating disorders, self harm, or addiction because of trauma and self-worth issues? Until you feel that your work has worth, as an extension of your own worth, you may be too paralyzed to create and share that work.
“Rejection in your personal life can easily translate over into the fear that your creations (the purest expression of you) will be rejected too.”
SELF-FULFILLMENT NEEDS
Self Actualization- reaching full potential through fulfillment of all other needs
The term self-actualization sounds so mystical and profound; to achieve self-actualization is to become the Buddha, to reach enlightenment and higher planes of existence. But, in the sense of Maslow’s hierarchy, self-actualization is much more simple and attainable than breaking the karmic cycle.
When speaking of Maslow’s hierarchy, the term self-actualization simply means generating an original idea, initiating the task to bring it to fruition, and seeing it through to completion. And, according to Maslow, this process of creation cannot happen unless you have met all the needs in the bottom four tiers.
Maslow described Self-Actualization as:
“It refers to the person’s desire for self-fulfillment, namely, to the tendency for him to become actualized in what he is potentially. The specific form that these needs will take will of course vary greatly from person to person. In one individual it may take the form of the desire to be an ideal mother, in another it may be expressed athletically, and in still another it may be expressed in painting pictures or in inventions.” (Maslow, 1943, p. 382–383).
He also identified 15 common characteristics of “Self-actualizers”:
- They perceive reality efficiently and can tolerate uncertainty
- Accept themselves and others for what they are
- Spontaneous in thought and action
- Problem-centered (not self-centered)
- Unusual sense of humor
- Able to look at life objectively
- Highly creative
- Resistant to enculturation, but not purposely unconventional
- Concerned for the welfare of humanity
- Capable of deep appreciation of basic life-experience
- Establish deep satisfying interpersonal relationships with a few people
- Intense or exciting “Peak” experiences
- Need for privacy
- Democratic attitudes
- Strong moral/ethical standards
How many of these traits do you have? If not, why? What are you missing from life that you need? How can you resolve this need? Who can help?
If you’re not writing, painting, creating, actualizing… stop and ask yourself- Are you unable to do so because one of your needs is not being met?
Are you struggling to survive?
Are you struggling to maintain your survival?
Are you isolated?
Are you mentally healthy?
Once we resolve the obstacles to our own unmet needs, we will be able remove the blocks in our creative endeavors.
Information on brain science, development, and learning provided from Help for Billy: A Beyond Consequences Approaching to Helping Challenging Children in the Classroom by Heather Forbes https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/17695490-help-for-billy
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs https://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html
Imposter Syndrome (APA) http://www.apa.org/gradpsych/2013/11/fraud.aspx
Executive Functioning https://organize365.com/adhd-affects-getting-organized-part-1/